Holographic Technology: Beyond Science Fiction

by Web Digital
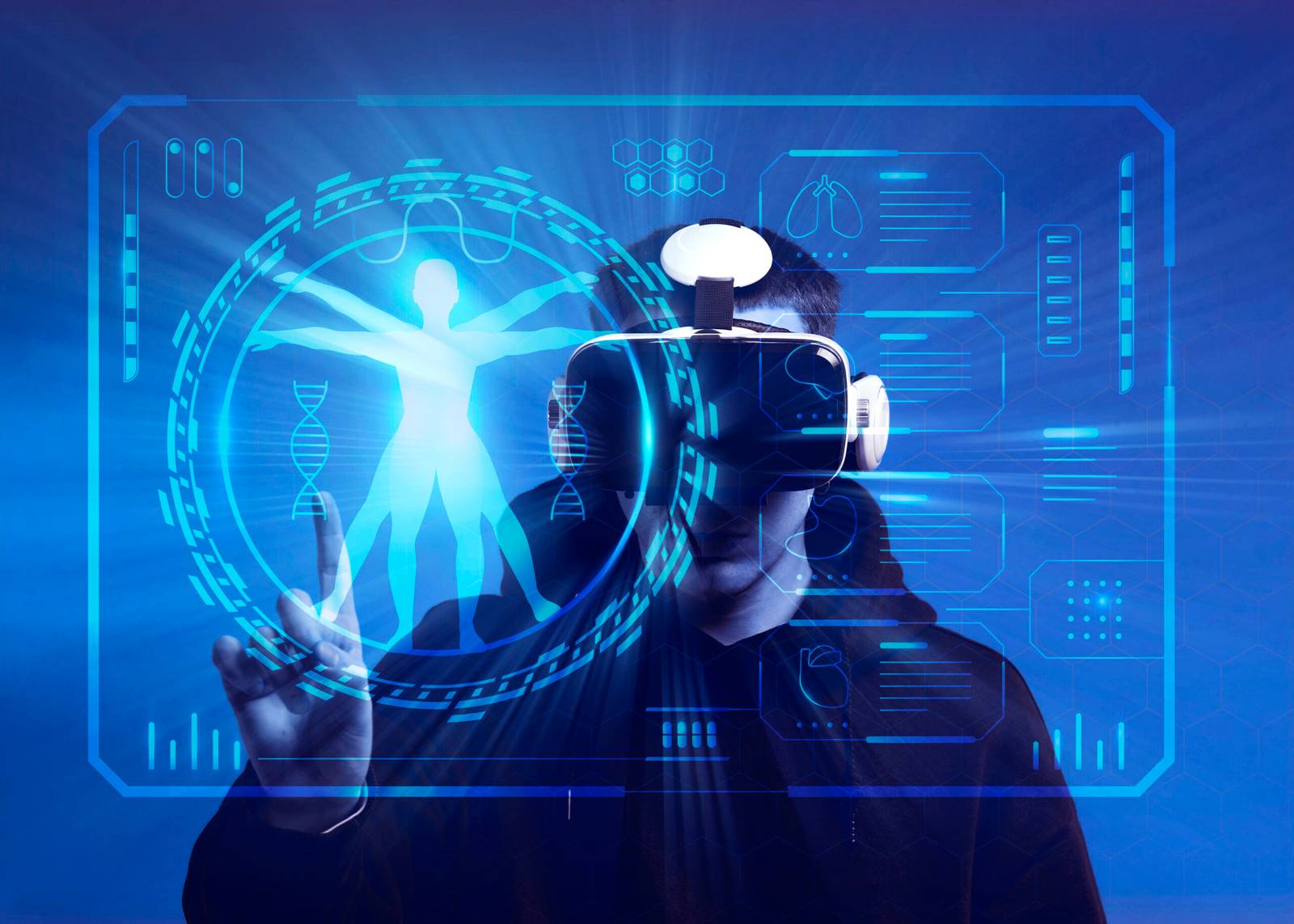
Once confined to the realms of science fiction, holographic technology has transcended the boundaries of imagination to become a tangible and transformative reality. This article delves into the evolution of holographic technology, its current applications, and the exciting possibilities it holds for the future.
Origins of Holography
Holography, the technique of creating three-dimensional images, was pioneered by physicist Dennis Gabor in the 1940s. However, it was not until the invention of the laser in the 1960s that holography became practical. Today, holographic technology has evolved far beyond its humble beginnings, finding applications in diverse fields.
Basic Principles of Holography
Holography involves capturing light patterns scattered from an object and using laser beams to create a three-dimensional representation of the object. Unlike traditional photography, holography captures both the intensity and the phase of light, resulting in images that appear truly three-dimensional.
Holographic Displays
One of the most captivating applications of holographic technology is in displays. Traditional displays are two-dimensional, but holographic displays offer depth and realism. Companies are developing holographic displays for use in consumer electronics, providing users with an immersive visual experience for gaming, entertainment, and even professional applications like design and modelling.
Medical Imaging Advancements
Holographic technology is making significant strides in the field of medical imaging. Holographic displays facilitate a more comprehensive understanding of complex anatomical structures, aiding surgeons in planning and performing intricate procedures. The ability to visualize three-dimensional medical images enhances diagnostic accuracy and surgical precision.
Holography in Education
Holographic technology is transforming the educational landscape. From holographic textbooks to interactive holographic lessons, educators are leveraging holography to make learning more engaging and immersive. Students can explore historical events, dissect virtual organisms, and interact with complex concepts in ways previously unimaginable.
Virtual and Augmented Reality Integration
The integration of holographic technology with virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) is expanding the horizons of immersive experiences. Holographic elements in VR and AR environments enhance realism and interactivity, creating virtual worlds that closely mirror the physical realm. This convergence is not only revolutionizing gaming but also finding applications in industries like architecture, training simulations, and remote collaboration.
Art and Entertainment
Holographic technology is leaving its mark on the art and entertainment industries. From holographic concerts and performances to immersive art installations, artists are pushing the boundaries of creativity. Holographic projections enable new forms of artistic expression, blurring the lines between the virtual and the tangible.
Security and Authentication
Holography has long been employed as a security feature in currency and identification cards. The intricate and unique nature of holographic patterns makes them extremely difficult to replicate, providing a robust means of authentication. As technology advances, holographic security features are becoming even more sophisticated, staying one step ahead of counterfeiters.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its remarkable advancements, holographic technology faces challenges. Current holographic displays often require specific lighting conditions, and the size of holographic projections is limited. Additionally, the development of affordable and scalable holographic solutions for widespread consumer use remains an ongoing challenge.
Future Prospects and Innovations
The future of holographic technology holds exciting prospects. Innovations in materials, optics, and computing power are driving the development of more accessible and versatile holographic displays. Researchers are exploring dynamic holography, enabling real-time changes to holographic projections, and quantum holography, which harnesses quantum properties for even more precise and complex holographic imaging.
Conclusion
Holographic technology, once a fantastical concept in science fiction, has become an integral part of our technological landscape. From captivating displays to transformative applications in medicine, education, and entertainment, holography is pushing the boundaries of what is possible. As research and development continue to unlock new innovations, holographic technology is poised to redefine our interactions with the digital world, opening doors to immersive experiences and practical applications that were once only dreamed of in the realm of science fiction.
Recommended Posts

Web Design Portfolio Tips for Canadian Freelancers
September 27, 2025

The Cost of SEO Services in Canada
September 27, 2025
How to Use Google Business Profile for Local SEO
September 26, 2025
